-
No products in the cart.

Chia Seeds 101 – Top 8 Health Benefits & How To Consume?

Who knew something as small as chia seeds could pack such a nutritional punch? Here in Singapore, where we’re always on the lookout for the next big thing in health foods, chia seeds have quickly become a must-have in everyone’s pantry. They’re not just versatile and easy to incorporate into any meal, but their health benefits are through the roof!
Chia seeds have emerged as a powerhouse of nutrition, offering an array of health benefits that can significantly contribute to a balanced diet. Packed with omega-3 fatty acids, Chia seeds can elevate your heart health, improve digestion and reduce inflammation. Perfect for topping off your breakfast or enriching your salad, chia, in all its forms, offers versatility and vast health benefits.
In this article, we dive deep into the world of chia seeds, exploring their nutritional content, health benefits, how to incorporate them into your diet, and how they compare to flax seeds.
What Are Chia Seeds?
Chia seeds are small, black seeds from the Salvia hispanica plant, a member of the mint family, which is native to central and southern Mexico. Notwithstanding their ancient history as a dietary staple, chia seeds have gained modern popularity as a superfood due to their impressive nutritional profile and health benefits.
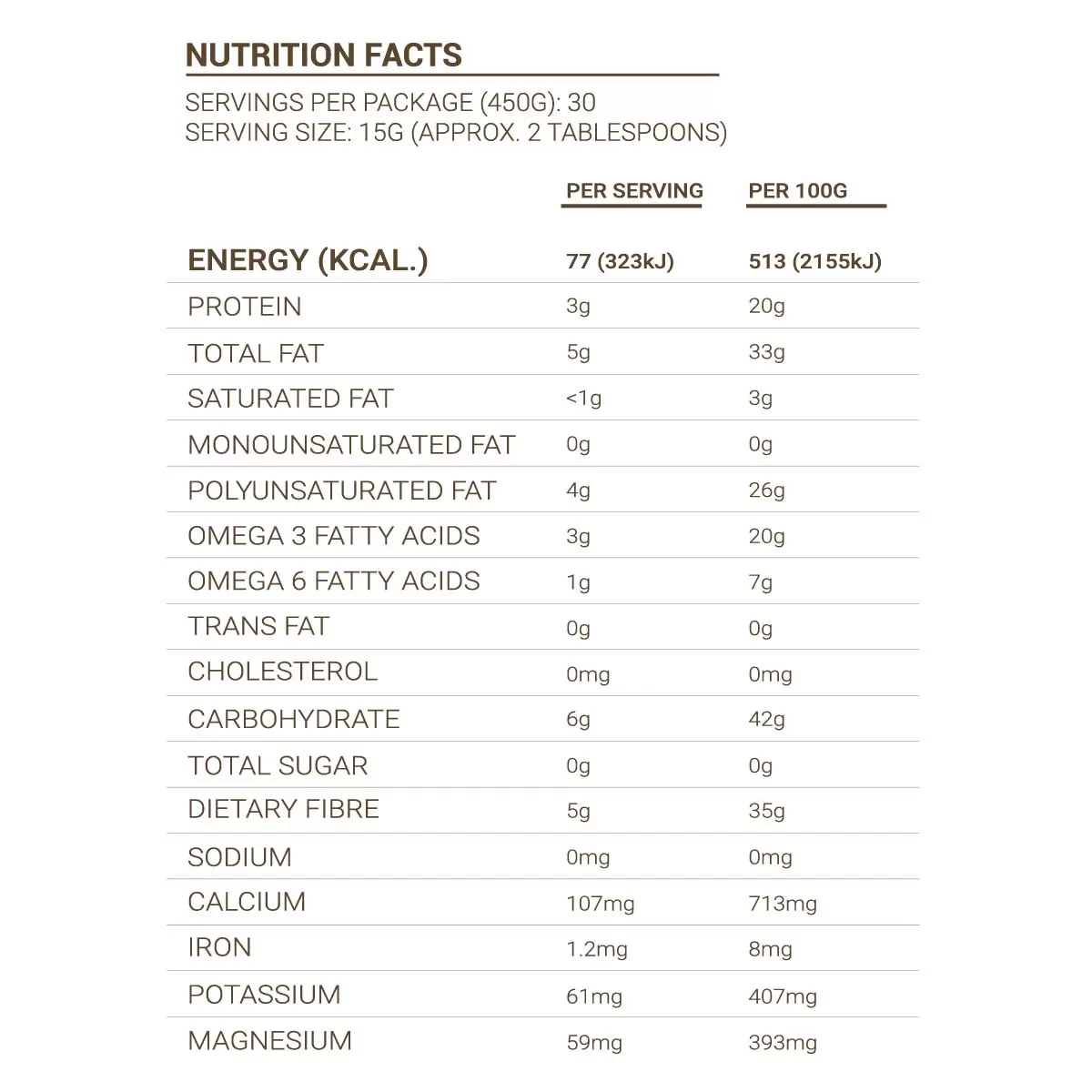
Chia Seed Nutrition (Per 2 Tablespoons or 15g):
Top 8 Health Benefits of Chia Seeds
- Enhance Digestive Health: Chia seeds are an excellent source of dietary fiber, offering about 5-6 grams per serving of 2 tablespoons. This high fiber content aids in digestion by promoting the growth of good bacteria or probiotics in the gut and ensuring smooth bowel movements. Regular consumption can help prevent constipation and maintain a healthy digestive tract.
- Enhance Heart Wellness: The omega-3 fatty acids in chia seeds, particularly alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), play a crucial role in cardiovascular health. These fats help to reduce blood pressure, lower triglyceride levels, and elevate HDL cholesterol, the “good” cholesterol. This combination of effects protects against heart attack, stroke, and atherosclerosis. You may read this article for more information.
- Strengthen Your Bones: Chia seeds are a rich source of calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus, minerals essential for bone health. To put things in perspective, about three tablespoons of chia seeds will yield more calcium than a glass of milk. This makes chia a great alternative for those who don’t consume dairy products. Together, these nutrients contribute to bone mineral density and overall skeletal health.
- Blood Sugar Control: Incorporating chia seeds into your diet can help regulate blood sugar levels, thanks to their high fiber and healthy fat content. These components slow down the rate at which complex carbohydrates are digested and absorbed into the bloodstream, preventing blood sugar spikes after meals. This regulatory effect can reduce the risks of metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes.
- Great For Weight Management: The combination of fiber and protein in chia seeds can significantly aid weight management efforts. Fiber absorbs large amounts of water and expands in the stomach, increasing the feeling of fullness and reducing appetite. Protein also helps promote satiety, which leads to eating less food without feeling hungry. Together, they can help control weight by minimising calorie intake.
- Inflammation Reduction: Chronic inflammation is linked to several health conditions, including heart disease, cancer, and autoimmune diseases. Chia seeds contain significant amounts of omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, which have been shown to reduce inflammation markers in the body, promoting overall health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
- Improve Energy and Metabolism: Chia seeds are packed with B vitamins, zinc, iron, and magnesium, all of which are involved in energy metabolism. Their balanced blend of protein, fats, and fiber can help stabilize energy levels throughout the day. For athletes or those looking to enhance exercise performance, chia seeds can be a beneficial supplement for sustained energy and improved endurance.
- Mood Enhancement: Tryptophan, an amino acid found in chia seeds, is a precursor to serotonin, a neurotransmitter that plays a key role in mood regulation. Consuming chia seeds may help improve mood and promote better sleep quality by facilitating the production of serotonin and melatonin, the sleep hormone.
How To Consume
Chia seeds are incredibly versatile and can be easily incorporated into your daily diet. Here are a few ideas:
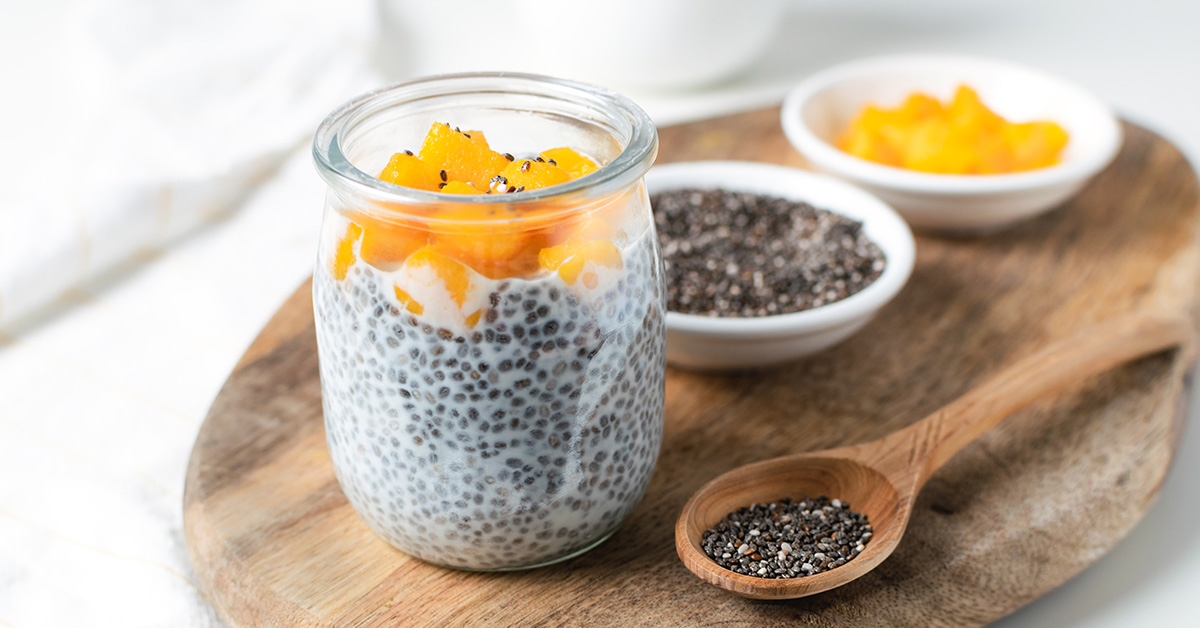
- Soaked in Liquid: Soak in water or milk overnight to make a chia pudding. For a quick recipe, you can also stir and soak chia seeds in water/beverages for a short period of time (at least a few minutes) to allow the seeds to bloat and absorb water before drinking the beverage.
- Added to Smoothies: Blend with fruits, vegetables, and liquid of choice.
- As an Egg Substitute: Mix with water to form a gel and use in baking. The general ratio for making a chia seed egg substitute is 1 tablespoon of chia seeds to 3 tablespoons of water. Let the mixture sit for about 5-10 minutes until it forms a gel-like consistency similar to that of a raw egg.
- Topping: Sprinkle on yogurt, salads, or oatmeal for a nutritional boost.
If you’re looking for more creative ways to consume Chia Seeds, check out the recipes here.
What ’s the difference between White Chia Seeds and Black Chia Seeds?
There is no major nutritional difference between the black and white seeds. Studies have shown that the difference is more related to where and how the seed was grown, the soil condition of the area, and not so much the seed colour.
Summary
Chia seeds are a nutrient-rich superfood that can enhance your health in numerous ways. From improving digestive health to boosting heart health and aiding in weight management, the benefits are as versatile as the ways to consume them. By integrating chia seeds into your daily diet, you’re not only embracing a superfood but also adopting a healthier lifestyle with a stronger immune system in the long run.
For readers in Singapore looking to improve their health and wellness, incorporating chia seeds into your diet is a simple yet effective step towards healthy eating for the whole family. Whether the seeds are added to water, smoothies or breakfast recipes, made into chia pudding, or used as a nutritious topping, the possibilities are endless. Start exploring the benefits and recipes of chia seeds today and make them a staple in your health-conscious diet.